
This image shows the brightest part of NGC 2264, a giant region of ionized hydrogen in Monoceros. The bright 5th magnitude star in the upper part of the center of this frame is S Monocerotis, it forms the base of the so-called Christmas Tree Cluster. The shape of this star cluster resembles a conifer, it is outlined by a dozen or so 7th magnitude stars and "stands" upside down, the tip being the 6th magnitude star at the apex of the "Cone Nebula", which is the designation of the dark nebula which protrudes into the southern end of the red emission area. The nebula itself shows a mixture of red and blue colors, the red ones indicating hydrogen emission and the blue parts indicating starlight reflected by the nebula's dust particles. There is also lots of substructure in the nebula, in some areas dark nebulae form intrusions into the red background nebulosity.
Both the Cone Nebula and the Christmas Tree Cluster were discovered by William Herschel in 1783.
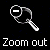 NGC 2264 - Cone Nebula Region, Wright-Newtonian photograph.
NGC 2264 - Cone Nebula Region, Wright-Newtonian photograph.
Exposure Data